- Risk Management
It is the process of Identifying Risks, evaluating them, Planning & Implementing Responses to Risks, and Monitoring all these processes
- Project Risk
An uncertain incident that may occur or has already occurred during any stage of project work is known as a risk. Also Knows ad an Unknown event which can have both positive or negative impacts on the project scope or any other aspects of a project.
- Positive Risk has a positive effect on the project outcomes. Aka Opportunity
- Negative Risk has a negative effect on the project outcomes. Aka Threat
- Risk Trigger
An event or condition that indicates that a risk is about to occur
vRisk: Poor Law & Order situation
Risk Trigger: Fiery speech by a leading opposition politician
- Risk Score
A quantity that indicates the ranking and level of a Risk –low, medium, or high. Obtained by multiplying Probability and Impact of a Risk
vThe Probability of a Risk is 5/10 and its Impact is 8/10. Its Score is 40/100.
- Known Risk (aka Known Unknown).
A Risk which has been Identified. A Known Risk is analyzed and provided with a Response
- Unknown Risk
Also considered as Unknown Unknown or Emergent Risk, An Unidentified Risk.
- Risk Category
A group of potential causes of Risk, like Physical, Acts of God, Design/Technical, Political, Environmental, Economic, Financial, Organizational, etc.
- Contingent vs Preventive Risks
Contingent risk management is when the problem occurs by chance, the plan set for encountering the problem is considered as ‘contingent’. And the plan that is made before any problem occurs is considered as risk preventive action.
- Contingency Reserves (CR)
Funds for dealing with Known Risks if they occur, also known as reserves for known risks.
- Management Reserves (MR)
Funds for dealing with any Unknown Risks if they occur
- Risk Analysis
The Identified Risks are analyzed, including their Probability and potential Impact on the Project, to determine which Risks warrant a Response
- Qualitative Risk Analysis
The process of assessing the Probability of Occurrence and Impact and other characteristics of Risks. This analysis helps prioritize the Risks into High, Medium & Low according to the Company’s criterion
- Quantitative Risk Analysis
The process of numerically analyzing the combined effect of identified individual project Risks on overall project objectives
- Risk Response Strategy
Strategy, commensurate with the Company’s Policy, on what to do with Risks; 5 each for Negative & Positive Risks
- Risk Owner
The person responsible for Monitoring the assigned Risk, its Trigger, and for selecting and implementing an appropriate Risk Response Strategy
- Risk Response Plan
The Plan of Action to handle a Risk (counter a Threat or accentuate an Opportunity.
Risk: Rain for an outdoor function
Response Plan: Move the function indoor
- Residual Risk
Risk that remain or may remain after application of a Risk Response
Residual Risk: In the previous example, guests will still get wet as they move from parking to the function hall
- Secondary Risk
Risk that arises, or may arise, after application of a Risk Response
vRisk: No expertise for a task on the project
Response: Outsource to a Seller
Secondary Risk: Seller goes out of business
Another Secondary Risk Example. On a construction project, the project manager has identified fire on the service lift as a possible risk. His risk response is to fight the fire using water. Now there is the risk of water flowing down the elevator chute into the basement where cement is stored. This water flooding the basement store is called as a secondary risk.
- Escalation Levels
Escalation levels are set of procedures placed to deal with potential problems in the context of the strain of the problems. Companies set levels to deal with such kind of problems.
Risk outside the project manager authority and outside the project scope is called escalation levels. It is to be dealt by higher management. A meeting to discuss the alternate solutions of a project risk occurred, with the point of whom the risk can be transferred.
A project manager says, “there is no point in recording the low-risk if does not affect the project by much”. But NO, all kind of risks must be recorded and put into watch list to check risk probability, its impact and to control them accordingly.
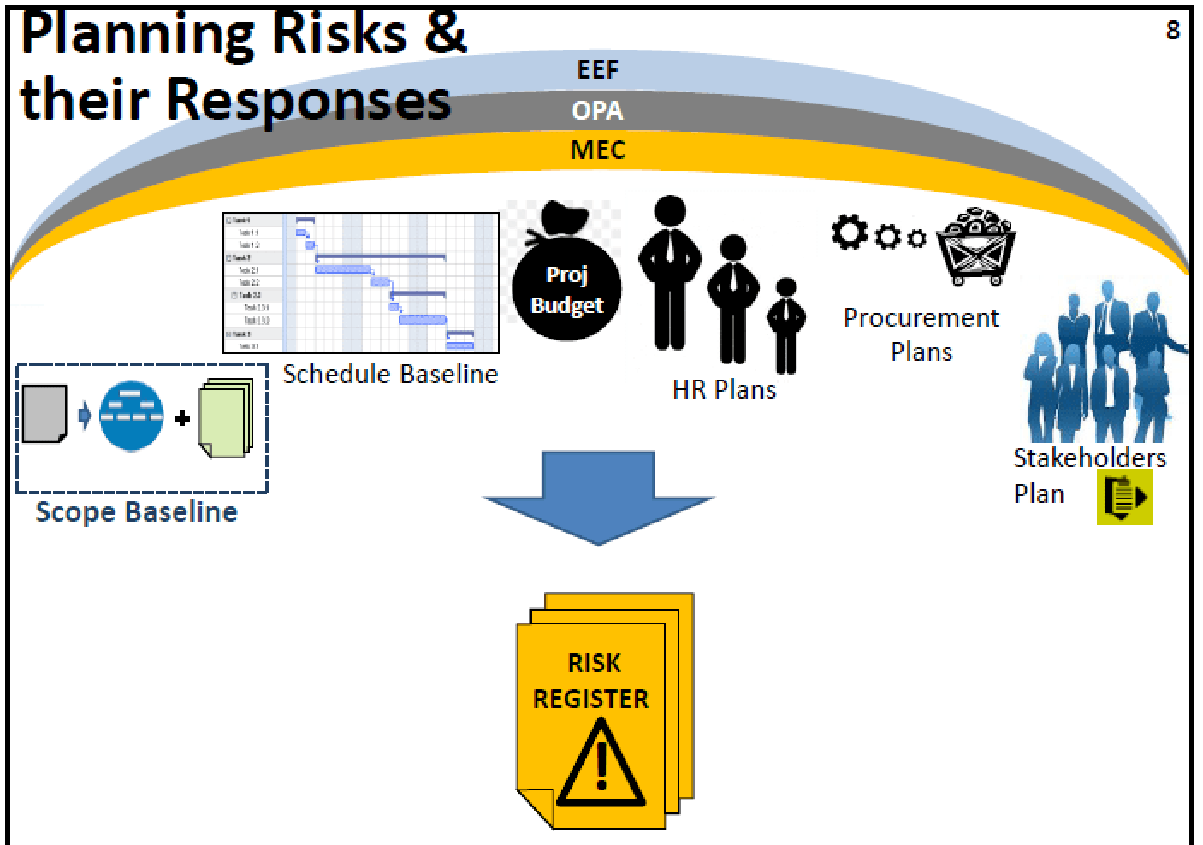
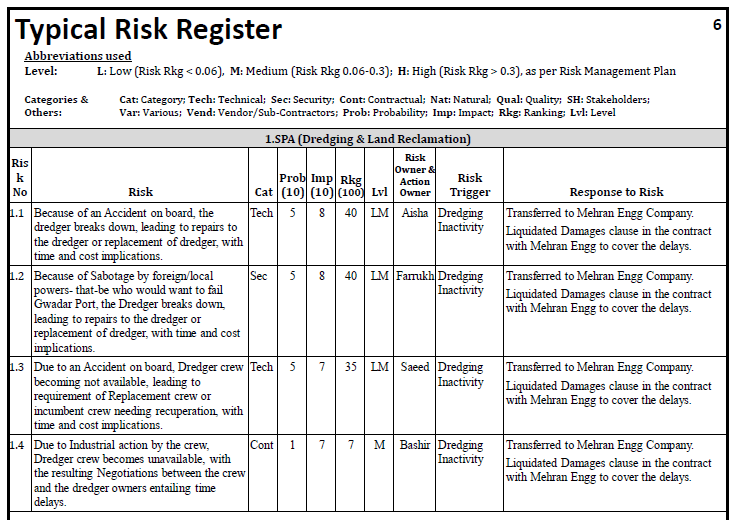
- Risk Register
A document which tabulates all the Known Risks and their actionable and management data. The key planning, implementing and monitoring document (page of a typical Risk Register on a subsequent