What is Satisfaction
“Satisfaction is an affective or emotional state following an evaluation of the consumption experience”. Dictionary definitions describe satisfaction as ‘fulfilment’ or to ‘be content or pleased’.
- Achieving mere satisfaction is not enough, the aim is to delight a customer if loyalty is to be achieved
- Satisfaction and loyalty
- Figure 4.3 depicts the benefits of having a highly satisfied customer
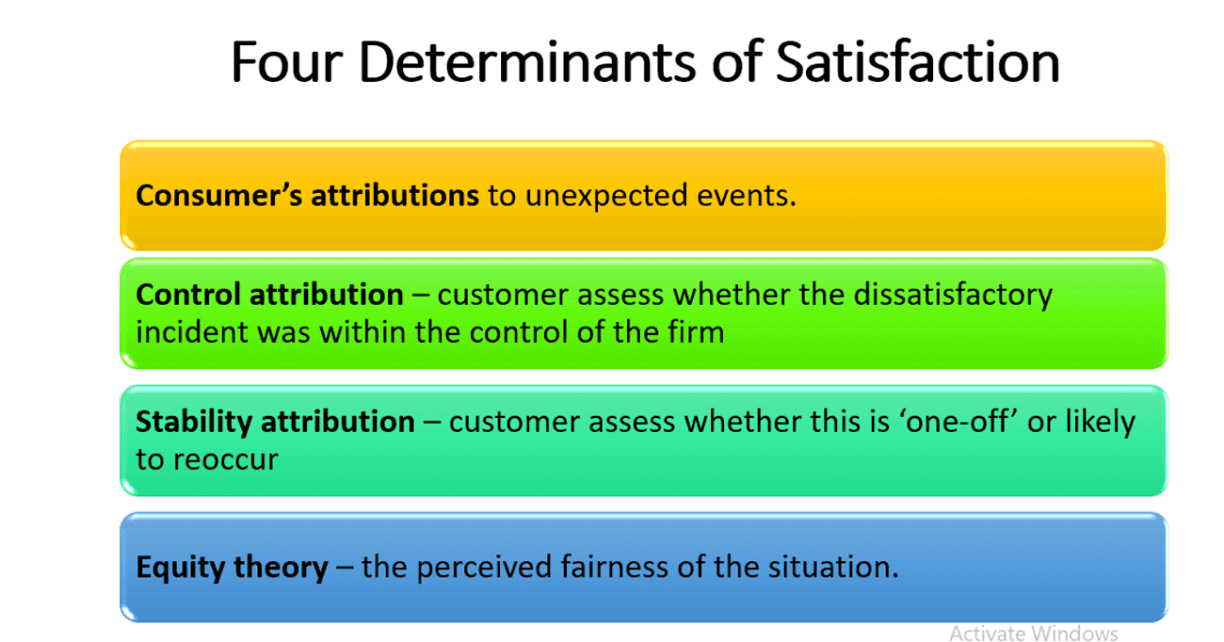
Four other determinants of satisfaction.
Prior attitudes toward the brand are thought to influence expectations. If previous associations and experiences are positive, customers will be more likely to forgive an unsatisfactory event.
- Consumer’s attributions to unexpected events.
- Control attribution – customer assess whether the dissatisfactory incident was within the control of the firm e.g. flight delay due to bad weather.
- Stability attribution – customer assess whether this is ‘one-off’ or likely to reoccur
- Equity theory – the perceived fairness of the situation. Try telling your class that all those students wearing wristwatches today will automatically get a High Distinction or A in your class.
First, the model shows that consumers compare their pre purchaseexpectations (or some other comparison standard such as desires) with perceptions of post-purchase performance. Next, it should be noted that the source of these expectations might come from advertising (or other forms of marketer-controlled communication) word of mouth, previous focal brand experience or indeed experience with competing brands.
Researchers might be encouraged to mention other factors that might impinge on this process such as prior attitudes, attributions, mood states, level of personal involvement and perceptions of fairness or equity.
In each case these factors might potentially act as either a moderator (intervening variable) between disconfirmation and satisfaction, or as a moderator variable (i.e., it alters the nature of the relationship between disconfirmation and satisfaction).
Finally, it is worth noting the ‘ratchet effect’ i.e., according to this model expectations must be continually exceeded if satisfaction is to be achieved. In doing so the firm inadvertently sets a new (higher) standard each time.
That is it raises the bar or the base level of expectations and so (theoretically) on each new purchase occasion the customer will expect the firm to meet or exceed the new (higher) standard.
Example: measuring and monitoring satisfaction levels (or service quality).
The first part is straightforward and most large organizations now have some form of satisfaction/quality tracking in place. However, the methods, frequency, and what is measured is likely to vary markedly from firm to firm. Regarding the second part of the question, again most large firms have some system in place to achieve this. However, the extent to which it is being done well might make for useful classroom discussion.
Cognitive Service satisfaction vs emotional service satisfaction example
Most services tend to provide elements of both cognitive and emotional (dis)satisfaction, but (like the intangibility continuum from previous article) some are more weighted more highly with one or the other. For example, entertainment such as movies or sporting events would provide for high emotional satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
Another example:
If purchasing the services of a funeral director, a great deal of the overall satisfaction gained from the experience would be generated from how well the funeral director tended to your emotional needs of sympathy, empathy, respect and reverence etc.
Cognitive satisfaction
It would be generated from services where it is important to execute the service correctly, and less important how the service performed. As an example, if you hired a tax accountant, you would prefer they legally minimize your tax owed, before catering to your emotional satisfaction.
Most services, however, have elements of both. If you are making the decision to hire the services of an obstetrician during you (or your partner’s) first pregnancy, you would not only want a doctor who perform emergency services perfectly if needed, but also someone who has a good ‘bedside manner’ and can smoothly guide you through some emotional times.