Recent research found in a study of hairdressers that customer loyalty was predominantly to the individual hairdresser rather than the firm.
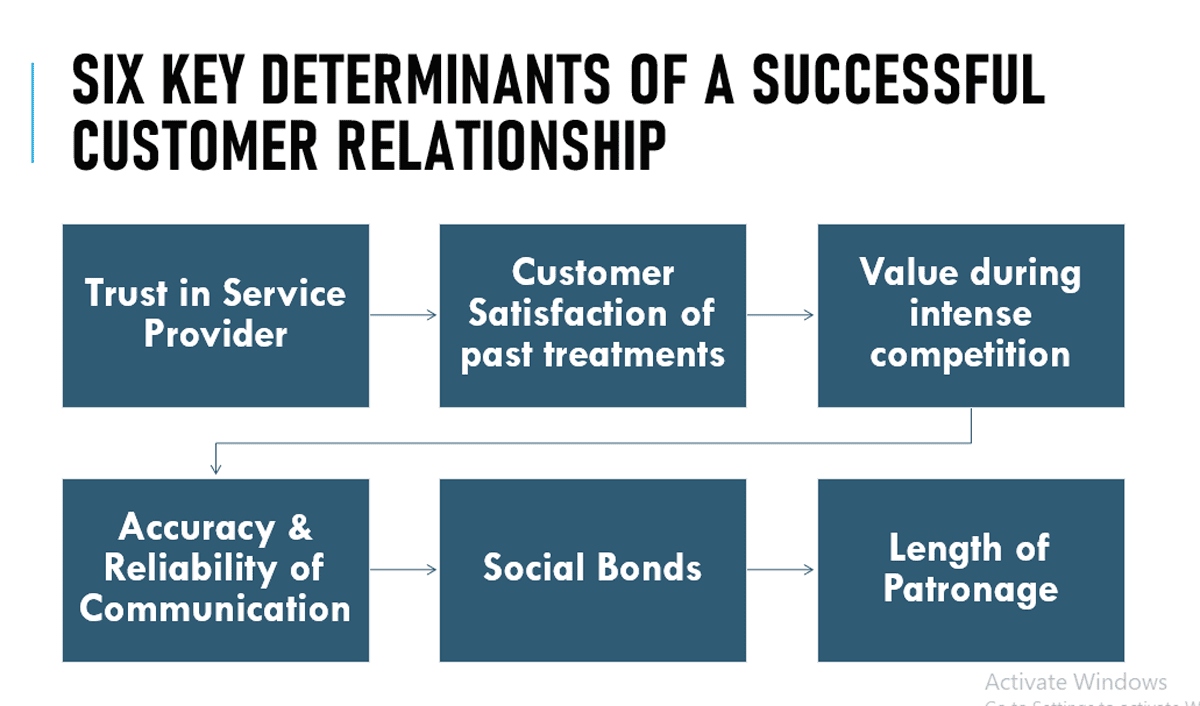
The key determinants of a successful customer relationship are:
Trust in Service Provider
The essential aspect for any organization is customer’s trust on its brand, it plays a vital role in building customer relations and managing them at higher levels.
Customer Satisfaction of past treatments
Influences relationship commitment because it insulates the organization against competitive offerings. See chapter 4 for a more detailed analysis of customer satisfaction.
Value during intense competition
Service firms that continually provide perceived value stand a better chance of retaining their established customers, even in the face of intense competition.
Accuracy & Reliability of Communication
Good communication, which includes empathy, responsiveness and product knowledge, helps to resolve any disputes and aligns the expectations of both parties.
Social Bonds
Friendship leads to higher commitment by both parties.
Length of Patronage
The longer a customer stays with a service provider, the stronger the commitment and the greater the psychological barriers to switching.
Reasons for Customer Defections
It is important to understand why customers defect. The most common reason is core service failure. Service encounter failures are ranked second in importance, and result in failures in the interpersonal interactions between server and customer.
Customers desire levels of courtesy, friendliness, professionalism, product knowledge, attentiveness and acknowledgement. Pricing problems constituting high prices, unfair policies and deceptive pricing is another reason for customer defection.
A firm that does not respond to a service failure in the appropriate manner also causes customers to find alternative suppliers. This needs to be addressed in terms of company attitude and staff training. Other reasons for customer defection include inconvenience, attraction by competitors and involuntary switching.
The Key Role of Employees in Customer Relationships
In a service setting all employees interact with customers. Each person, therefore, contributes or detracts from the image and reputation of the service organization that they represent, and exercises a direct influence on how relationships are formed, and the quality and durability of those relationships.
Consequently, we may say that in a service organization every employee has an important relationship marketing role to play and fulfil. Because of this employee retention is as important as customer retention.
Long-term employees gain a more thorough understanding of a firm’s systems, get to know customers better, build social bonds over time, gain the trust of customers, and often are a principal reason for repeat patronage and customer retention.
This has significant implications for recruitment, staff training and development, job empowerment and career planning. Also, of importance are staff recognition and reward programs.
Note:
The importance of staff, the key distinction between high-contact and low-contact personnel, and the implications of this, in a service setting cannot be over-emphasized.
Many, if not most, service organizations rise or fall, succeed or fail on the nature, personality, customer orientation and professionalism of their people and their ability to interact well with customers and with other members of staff. This is something that should be stressed with students, with reference to examples of good and bad service delivery.
Concluding Notes
Marketers should learn that a well-planned relationship marketing program has many advantages: to a firm and to its customers. Students should also understand the distinction between relationship marketing and loyalty programs, how mutually beneficial relationships are established and maintained, and that organizations need to be selective about the customers with whom it seeks to cultivate a relationship.
Finally, it should be emphasized that relationship commitment and loyalty is contingent upon:
- satisfaction
- trust
- value
- mutual trust
- effective communication
- social bonds