By drawing upon work by Levitt, Shostack, and Gronroos its identified that a service product strategy is constituted of core and supplementary elements. Furthermore, the latter classification may be sub-divided into two distinct categories: facilitating and supporting services.
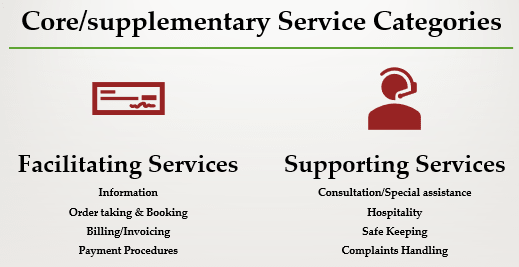
Core/supplementary Service Categories
Examples of each are provided and discussed below in some detail under the collective heading of supplementary services.
- Supporting services augment, enhance and add value to the core service offering, and serve to differentiate service organizations offering the same basic core service.
- Facilitating services, as the name suggests, enable, and are indispensable to, delivery and consumption of the core and other supplementary services.
Broad categories of facilitating and supporting services may be summarized in the following way:
Facilitating services Supporting/Enhancing services
* Information * Consultation/Special assistance
* Order-taking & Bookings * Hospitality
* Billing/Invoicing * Safekeeping
* Payment procedures * Complaints handling and
dealing with special requests
Developing a portfolio of service offerings
The term “service product portfolio” can be defined and used in one of two ways: it can refer to the range of supporting services offered, and it can refer to the number of product lines offered by a service organization.
Augmenting a core service product with a range of supporting services provides a firm with the enhanced wherewithal
- To offer more to the target market(s) it serves and, thereby, to add value to its product strategy;
- To differentiate itself competitively;
- To better cater for customer needs and requirements;
- To promote itself;
- To bundle or unbundle some of these supporting services;
- To charge premium prices for the core service;
- To develop and deliver ancillary spin-off services;
Examples of a Service Product Portfolio
Related service product lines provide a service firm with the means to target multiple markets. The Marriott example discussed in the text is a clear instance of this. Other examples include the range of different savings and loan accounts and rates offered by most banks;
- Different restaurant options in large hotels
- Airline classes
- University and TAFE courses
- Tour package options offered by travel agents
In addition to providing the means of market development, other reasons why service providers grow and develop their service product portfolios in this way include
- to grow the business
- to provide the means by which incremental sales and revenue can be generated
- to counter or pre-empt competitors
- to spread business risk
- to create or enhance operating economies of scale
Creating New Services
The article explains several main avenues of service creation. These include:
- Innovation – in core and/or supplementary services offered
- Process innovation
- Imitation (alternatives to extant services)
- Service product and/or process line extensions
- Improvements to the core and/or supplementary service products offered
- Style changes