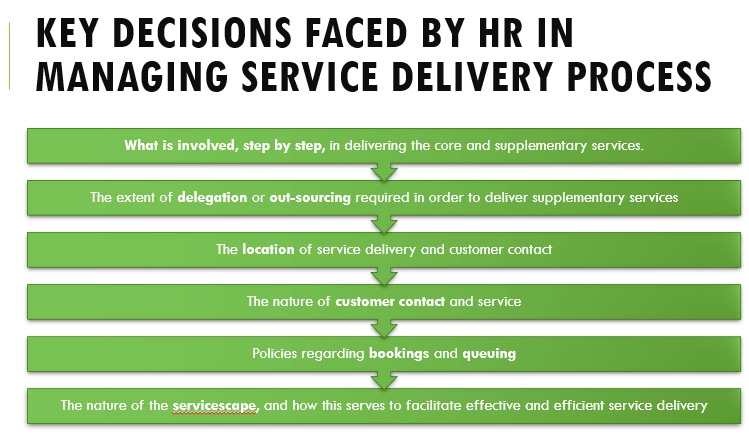
Above mentioned figure summarizes key decisions faced by management in planning and configuring the service delivery process. Essentially these may be summarized and discussed under six main headings:
(i) What is involved, step by step, in delivering the core and supplementary services.
Note: Shostack’s article on flowcharting or blueprinting illustrates well how this task may be undertaken. A useful task for students is to apply this process to a service organization of their choice. The first applied question the end of this chapter invites students to undertake this task.
(ii) The extent of delegation or out-sourcing required in order to deliver supplementary services
(iii) The location of service delivery and customer contact
(iv) The nature of customer contact and service
(v) Policies regarding bookings and queuing
(vi) The nature of the servicescape, and how this serves to facilitate effective and efficient service delivery
Other key issues that warrant attention in this context include:
- Implications for human resource management
- The role increasingly played by technology in the process of service delivery
- The need to identify potential problems, errors, bottlenecks and “moments-of-truth” in service delivery, and to formulate contingency plans for dealing with them effectively
- The extent of variation, customization and flexibility that needs to be provided for within an otherwise routine or tightly formatted service delivery process
- The balance that needs to maintain between service delivery efficiency from an operations and management perspective, and the customer’s need for time attention satisfactory to their purposes.
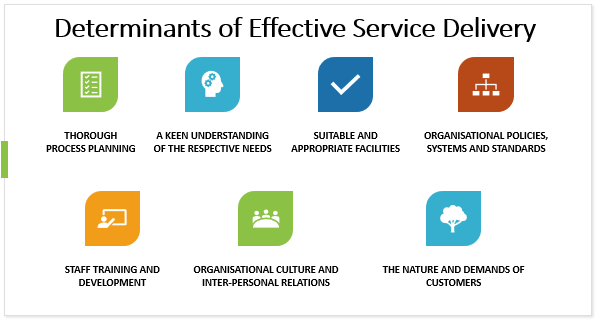
Determinants of effective service delivery
Effective service delivery is determined, inter alia, by:
- thorough process planning
- a keen understanding of the respective needs and requirements of customers and staff alike
- suitable and appropriate facilities
- organizational policies, systems and standards, and the manner by which these are implemented and maintained
- staff training and development
- organizational culture and inter-personal relations
- the nature and demands of customers, and how they are accommodated
The Role of Intermediaries
Here we discuss ways by which service delivery may be delegated to external representatives or agents, and managerial implications arising from this. Key managerial considerations include:
- How to maintain control over what is delivered, and how
- How to maintain consistency in what is delivered, and how
- Inter-organizational communications
How to achieve synergy within the inter-organizational culture
Productivity in a Service Setting
Key points to be emphasized here include:
- Reviewing tasks to be performed, and/or restructuring the ways in which tasks are performed, can significantly increase output and improve cost effectiveness and efficiency.
- Technology provides opportunities to streamline and to improve the productivity and cost efficiency of what is done backstage.
- Productivity and cost efficiency improvements should not be considered without reference to the affect or impact on the service product(s) offered and the means of service delivery, and the consequent affect on customers – e. their likely response.
- When customers are involved in the service production process, management should examine how customers’ inputs can be made more productive – e. so that they don’t clog up or slow down the service delivery system in a way that adversely affects other customers and profitability.
- Productivity can often be improved by reviewing and responding better to variable patterns in customer demand.