Emotional Labor
Emotional labor concerns the management of emotions by service personnel so that customers will only see desirable expressions. An example would be a front desk manager of a hotel retaining a calm and professional appearance even when being abused by an irate guest.
Role Conflict
Role conflict is where service employees must manage the incompatibility of what customers desire, and the goals of management.
An example would be an emergency room doctor who is required to see as many sick patients as possible during their shift but is held up by some patients who demand more of their time.
Another example is that of a flight attendant who is expected to attend to passenger’s food and beverage needs but is also responsible for passenger safety and must ensure that passengers follow the rules of airline travel.
Role Ambiguity Example
Role ambiguity occurs when service employees do not fully understand the expectations required of them, and where they do not have all the information and resources necessary to fulfil their role. An example of role ambiguity could be if a restaurant guest requests a menu substitution, and the waiter does not know if the chef will agree to prepare this item.
Most employees embrace a level of role ambiguity as it can add interest to their jobs, but too much ambiguity can cause stress.
List of five organizations that require employees to exhibit emotional labor
This list is not exhaustive, and many examples can be given. Organizations that require employees to exhibit emotional labor would come from companies in industries such as:
- Air travel services
- Restaurants
- Hotels
- Entertainment
- Education
Service Personnel Stress Factors
This stress is due to:
- Emotional Labor – service personnel often have to manage their own feelings so that the public display is one of professionalism and courtesy.
- Role Conflict – when the goals of the customer and organization are in conflict, boundary spanners are expected to satisfy both.
- Role Ambiguity – some service personnel work in complex situations and may not always know what is expected of them
- Role overload – to deal with variable demand, and because services cannot be warehoused, employees are often subjected to work overload in peak periods.
- Service climate – the employee perceptions of management policies, practices and procedures.
Example of a high degree of emotional labor
This answer will depend on the organization chosen. As an example, flight attendants are often required to keep a professional outwards appearance.
Ways to Minimize Burnout
To minimize burnout, management could:
- Schedule long breaks between shifts
- Give the employee authority to deal with out of control customers
- Recognize that emotional labor is part of the job and train attendants accordingly
- Educate passengers that attendants should be taken seriously
Empowering Service delivery strategy
Empowerment has been described as ‘turning the front line loose’. It is most suited in-service businesses where there is:
- High customization and need for personalization
- Relationship marketing is important
- Service is non-routine and complex
- The business environment is unpredictable
- Employees have high growth needs and possess high interpersonal skills.
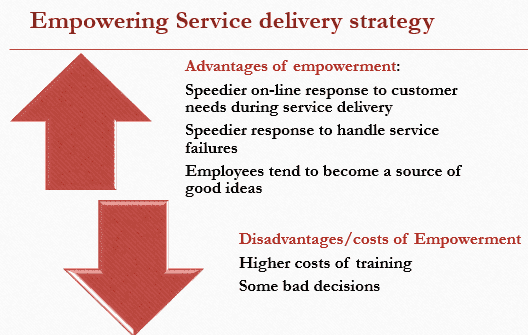
Advantages of empowerment:
- Speedier on-line response to customer needs during service delivery
- Speedier response to handle service failures
- Employees tend to more likely to interact with customers with warmth & enthusiasm
- Employees tend to become a source of good ideas
Disadvantages/costs
- Higher costs of training
- Some bad decisions