Industry Analysis: What is it?
To understand the competitive dynamics of an industry, businesses and analysts conduct industry analyses. An industry’s current state can be understood by using it.
To illustrate,
- Within an industry, the degree of competition
- Whether the industry is competitive
- Other emerging industries and the industry’s level of competition
- In light of technological advancements, the industry’s future prospects
- Industry credit systems
- Influences external to the organization
Analyzing a company’s competitors is the purpose of industry analysis. In addition to understanding current trends and opportunities within the industry, they also gain insight into potential threats.
You will be able to survive in this ever-changing business environment if you understand and use your differences from your competitors.
An overview of industry analysis types
Industry analysis can be performed in three ways. They are as follows:
- Porter’s 5 Forces Model
- PEST Analysis)
- SWOT Analysis
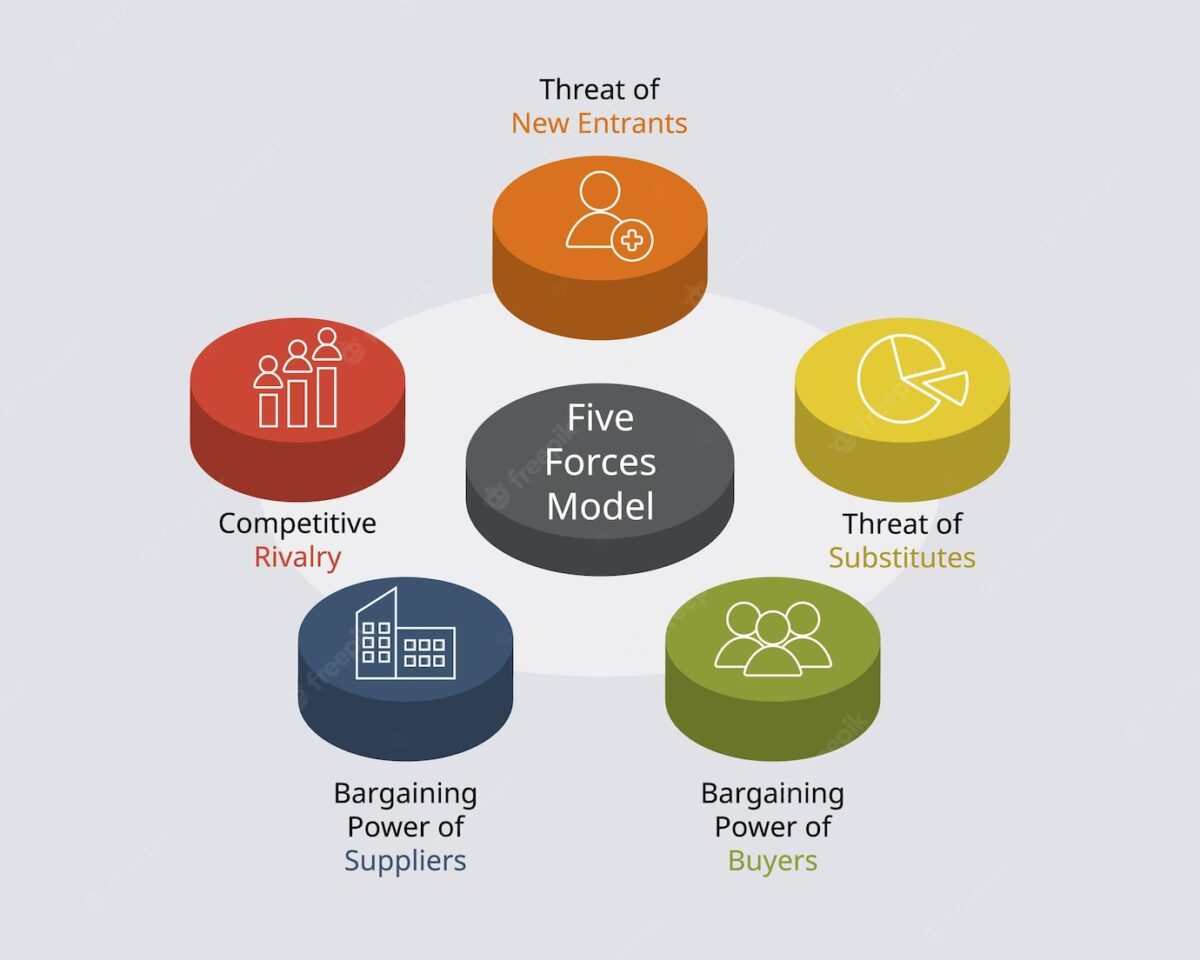
Porter’s Five Forces Model
In his 1980 book “Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors,” Michael Porter introduced Porter’s 5 Forces model as one of the most famous models ever developed for industry analysis.
Analysis of the five forces gives a better understanding of the industry and facilitates analysis, according to Porter.
This five-force model and another force – complementary good and service providers – are covered in our Corporate & Business Strategy course
1. Rivalry within the industry
A direct measure of an industry’s competitiveness is the number of participants and their market shares. Each of these factors directly affects the other. There is a tendency for competition to be more intense when products are not differentiated. It is also harder for competitors to compete because of high exit costs and restrictions imposed by governments, labor unions, etc.
2. Potential entry threats
New firms can easily enter a particular industry based on this indicator. Companies face the constant threat of new competitors if entry into an industry is easy. Those companies with little competitive advantage will benefit for longer if it is difficult to enter the market. In addition, companies face constant competition under difficult entry circumstances.
3. Suppliers’ bargaining power
Suppliers’ bargaining power is discussed here. A few suppliers have considerable bargaining power when the industry is dependent on a limited number of suppliers. Due to its direct influence on the quality and price of the final product, this can be particularly problematic for small businesses.
4. Buyers’ bargaining power
Customers have more bargaining power when they have more bargaining power. When consumers/buyers have market power, they can bargain for better quality, lower prices, or additional discounts and services. One example is an industry with many competitors but with a large share of sales accounted for by a single buyer.
5. Substitute goods and services threat
Whenever an industry produces a similar substitute product, there is competition from another industry. In this sense, there are potential competitors from other industries for all firms in that industry. The result is that they can no longer charge exorbitant prices, affecting their profitability. There are two types of substitutes – products offering the same functionality but a lower price, and products offering the same quality but a higher price.
PEST Analysis (Broad Factors Analysis)
PEST, or Political, Economic, Social, and Technological Analysis, stands for Broad Factors Analysis. An external environment can be analyzed using PEST analysis.
A PEST analysis uses four components to analyze industries. An analyst analyzes each component separately. Among them are:
1. Political
Political factors that impact an industry include specific policies and regulations related to things like taxes, environmental regulation, tariffs, trade policies, labor laws, ease of doing business, and overall political stability.
2. Economic
All of the factors which affect the economy, such as inflation, foreign exchange rates, interest rates, GDP growth rates, capital market conditions, and access to capital, are significant.
3. Social
Health, fashion, and social trends are three examples of behavior trends that are impacted by social trends in a particular industry.
4. Technological
In PEST analysis, the technological aspect takes into account advancements such as the Internet that change how people live and how businesses operate.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats are the four components of the SWOT analysis.
In addition to summarizing various industry forces, it can help determine how they impact a business.
1. Internal
The current position has been influenced by internal factors that already exist and may continue to do so.
2. External
A contingent event is an external factor. Depending on their likelihood and possible impact on the company, assess their importance. In addition, consider whether management is capable of pursuing the opportunity and avoiding the danger.
Analysis of industry is significant
In order for a business to understand the current market situation, industry analysis is crucial. As a result, financial returns from the business are forecasted in relation to demand and supply.
In addition, it indicates the industry’s competitiveness and entry and exit costs. The planning of a small business is very critical.
Analyzing an industry helps to determine whether it is still growing and has room for growth, or if it has reached its saturation point and is no longer growing.
Entrepreneurs can discover untapped opportunities by studying the industry in detail. Getting a positive result with industry analysis is not always guaranteed, as it can be subjective.
Entrepreneurs may make wrong decisions if they interpret data incorrectly. As a result, collecting data carefully becomes crucial.